RISK Criteria
As part of all risk management requirement, criteria for risk acceptance as well as criteria for performing risk assessment shall be defined. This module allows criteria to be defined in RiskClipper™ G7.
Implementing a Responsibility Centric, Closed-loop Risk Management Framework supported by Risk Control Database.
As a standalone program, the act of performing risk management is a fulfilment of regulatory compliance. However from a holistic information security management perspective, it demonstrates that the Management is driven by the minimum level of institutional forces (i.e. regulative). This level will only enable the Management to drive a compliance-based security culture within the Organization. Compliance-based security culture is primarily built on lagging indicators and is reactive in nature, which is insufficient to combat the wave of cybersecurity and information security threats today. Management need to step up and proactively lead the Organization foster a cultural-cognitive based security culture and edging towards a generative security culture maturity level.
Security culture can be built through a combination of correct implementation of frameworks institutionalized within the Organization and one of the main pillars would be the risk management framework. Besides providing assurance to the authorities and public communities that proper due diligence has been carried out to reduce uncertainty in business operations, the risk management framework should encourage the participation of the operational staff identifying risks that may affect their performance and the mitigating efforts invested, communicating the risks to the Management, sharing of knowledge and best practices among staff as well as getting staff to be responsible for their role to operationalize security practices. This outcome will drive sustainable risk management program to upkeep the quality and currency of risk management performed.
Maximus believes that everything in existence possesses an inherent set of vulnerabilities. Things of the same category would have an identical set of vulnerabilities. For example, humans inherently carry an observable risk of falls because we are bipedal and applications inherently carry a risk of being remotely exploited because it accepts requests from a sender to perform a task. Every vulnerability can be mitigated with a standard set of controls for things of the same category.
Depending on the risk discipline (e.g. cybersecurity), things of relevance may be a business process, application, operating system, physical infrastructure or an engaged outsourced service. While thing of relevance may bring benefits to the Organization, it may fall short of expectation after some time or be successfully exploited by bad actor. The antecedent for such consequence is the threat. While threats may be quite static in nature, threat events evolves over time. An example of a threat would be a malware attack, convention threat events would be sending file attachments with malware embedded but recently, the new threats would be embedding malware in PowerShell scripts.
According to risk management literature, each threat or threat event needs to exploit the vulnerability to form a risk, which in turn has a set of controls for risk mitigation. However, the main difference is that while all controls in the respective vulnerabilities may be applicable for a threat, not the same can be said for threat event. Threat events are generally more specific and trending in nature and hence, only certain controls may deem to be applicable for mitigating a risk.
Aspired to be an operational risk management tool, RiskClipper™ G7 has the following modules to enable risk management activities to be carried out effectively. A brief description of their functionality are described below:
As part of all risk management requirement, criteria for risk acceptance as well as criteria for performing risk assessment shall be defined. This module allows criteria to be defined in RiskClipper™ G7.
Referencing the design philosophy of RiskClipper G7, the security characteristics of the things of relevance (i.e. assets) need to be identified in order for proper threat modelling analysis to take place including identification of attack vectors and design weaknesses. As such, SPM will provide a unique representation of the system and network devices across production, staging and development environment, associates how business processes are involved in managing or using these system and network devices, and a detailed understanding of the access profile types and communication path aligned with zero trust principles.
Knowledge Base (RCKB)
In order to achieve a quality set of risk assessment, risk assessors must have the aptitude and attitude to carry out the risk activities. Unfortunately, most assessors lack the aptitude even though they may have acquired the necessary knowledge of a subject matter. RCKB can be viewed as a collective database of known risk and control and will be used as the starting point when performing risk assessment. This has been proven to be a valuable tool because even if the assessors lack the aptitude, the system will be able to generate all relevant considerations for assessors to perform risk assessment.
Risk Management (ORM)
This module enables assessors to build risk scenarios, perform risk assessment and risk treatment. It interacts with BAM and RCKB module to generate the relevant risk questions in which assessor responses are subsequently captured.
Board
As risk scenarios may not provide the full context on how an attack or a lapse is made possible, this modules pieces the various risk scenarios identified in ORM to simulate an attack or a lapse to an operation. Risk can then be holistically assessed and understood by the assessors.
Maximus advocates the concept of one risk management effort, multiple risk views. In this module, reports can be customised based on reporting needs by corporate, authorities, customers and/or partners. Templates can be configured so that the reporting can achieve consistency.
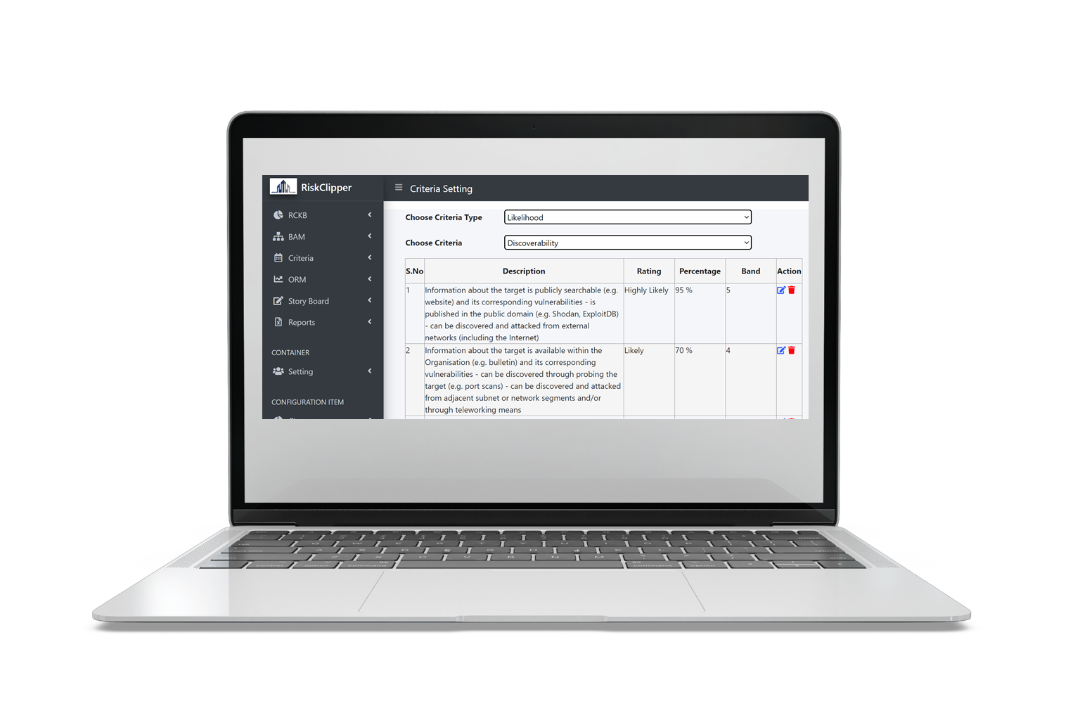
The system is not restrictive to a defined set of likelihood or consequence criteria. Both criteria and the corresponding scale description are aligned to organizational requirement. Note that though assessor may only see rating, the actual computation is based on the percentage assigned. This design is intentional so that equidistance between scales does not become a restriction to how Organization perceives from a quantitative perspective.
As a note, control strength criterion refers to the strength of a control implementation. One would agree that situational and technological constraints may restrict the degree of implementation. Hence, rather than a binary value, this feature allows assessors to provide clearer responses.
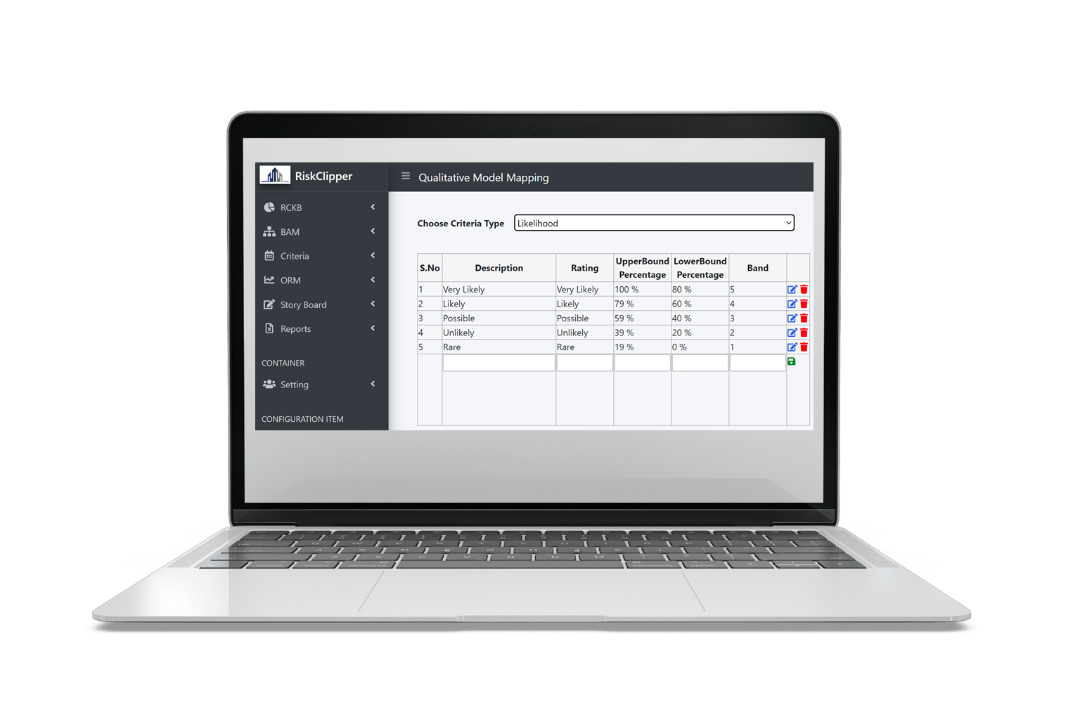
Again, flexibility is provided so that equidistance between scales does not become a restriction to how Organisation perceives from a quantitative perspective.
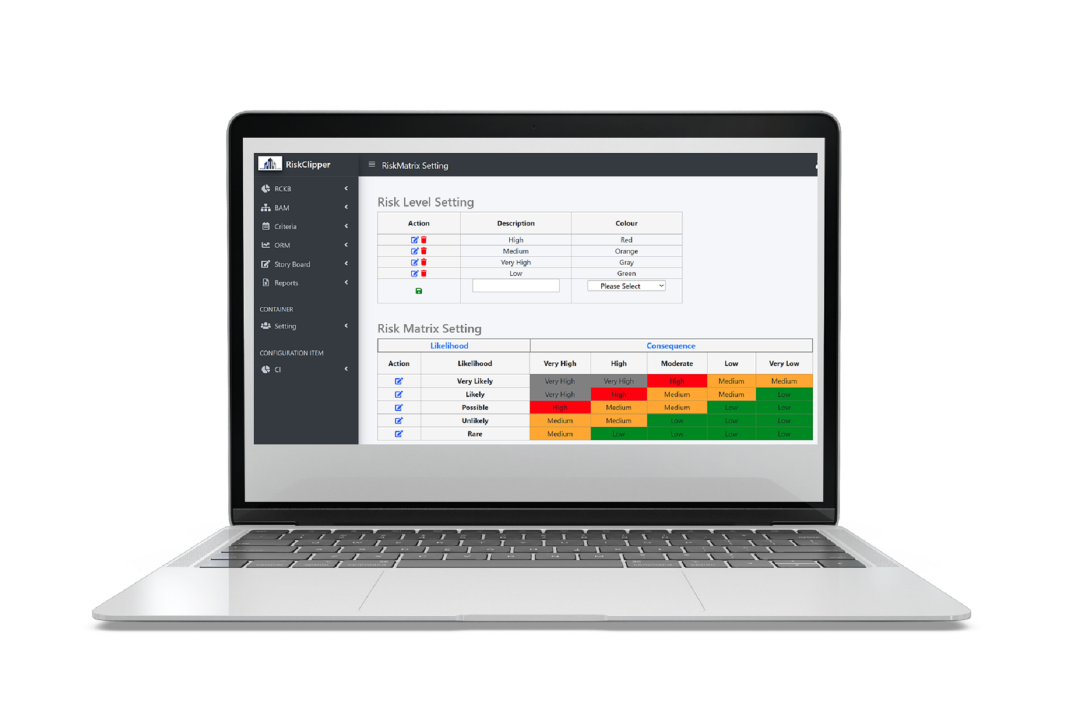
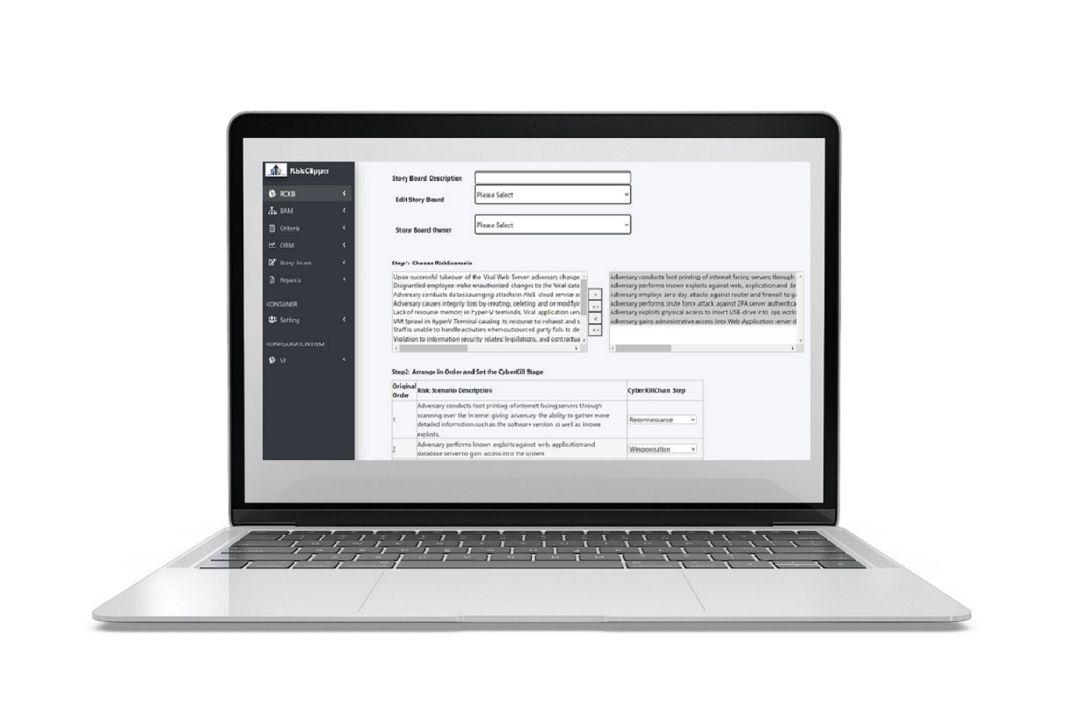
Every company is unique. That’s why every deployment we made are tailored to our customers' unique operating environment.
Automation: Through the capturing of security information, This feature allows configuration and validation of firewall rules.
Supports ATV and Risk Scenario Approach: Able to support both ISO/IEC 27001 and NIST recommendations.
Systematic Risk Impact and Inherent Levels Assessment: Through the implementation of DER concept as well as frequency of threat occurrence, this feature enable assessors to assess the impact and inherent risk level of the risk scenario with more accuracy.
On-demand Project Status: One of the biggest challenges is to complete risk management on-time; RiskClipper allows instance/project administrators to call upon this function anytime to identify the bottleneck.
Clear Risk and Control Ownership: Most risk management is conducted in a collective fashion and responsibilities are often unclear; RiskClipper is able to assign risk and control to individuals.
Strong search capabilities: With this feature, all objects in the database can be easily searchable for further analysis
Notification and Reminders: With the feature, risk assessors can be constantly reminded through emails until he/she completes her task.
Managing Multiple Risk Assessments: As risk management is often mandated to be carried on a regular interval, this feature helps to automate initiate the risk activities.
RCKB (Security) built on international standards: RCKB is built on international standards like ISO/IEC 27002, 27019, NIST, etc
Localising of RCKB.
Interpretation: RiskClipper allows assessors to re-write the applicable practice in their own business context
Maintaining assessment to be current with changing RCKB: RCKB is able to track the changes made and then prompt assessors to relook into the recommended practices.
Objective Risk Reporting: Using the multiple parameters to compute risk and supported by RCKB, the risk reported will be objective and fair.
Default Reporting Templates: RiskClipper is equipped with default reporting templates as appropriate according to the support level including risk reports, risk program management report, etc
Risk Treatment and Follow-up: RiskClipper tracks risk treatment items for approval and thereafter follow-up to close the risk treatment plan. If other business process management (BPM) modules are purchased, the effectiveness of the risk treatment tracked and verified.
With a streamlined workflow and expert guidance, RiskClipper™ automates the entire risk assessment and compliance process, end-to-end. Let’s explore how RiskClipper™ G7 can fit your exact needs.